Transformations
It is possible to edit objects all at once using geometric transformation. In SPAT Revolution, these transformations are mathematical laws used to distribute points (in our case, speakers) in the space, and can be used in either speakers or sources. In other words, it can help to create circles, spheres, or lines of speakers in seconds instead of minutes.
Sources Transformations
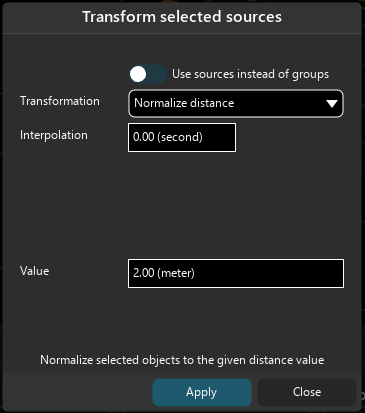
As with the custom speaker arrangement editor, we can apply some transformations to one or multiple sources. This feature is especially handy if you wish to quickly set sources on a circle or to put a selection of sources at a given distance for example.
To open the transform menu, right-click on a source in the source panel and choose “Transform.” You can also use the shortcut CMD/CTRL + SHIFT + T.
Sources’ transformations also include an integration time which allows to create a smooth transition between the current and the new source position. It also allows to choose to take into account groups, or sources contained on them.
Speaker Transformation
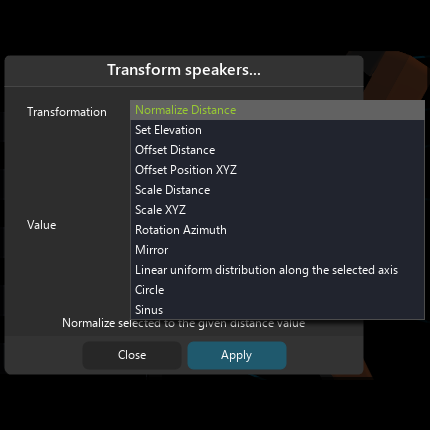
To modify a speaker arrangement with a predefined action, you can use the “transform” menu. To access it, click on the Transform button. A pop-up window will appear.
Normalize Distance: The further speaker will be placed at the given distance. All the other speakers will be placed at a relative distance from it.
Set Elevation: The first ring of speakers will be placed at the given elevation.
Offset Distance: This transformation applies an offset to the distance parameter of all speakers. It preserves the relative position of speakers.
Offset Position XYZ: Same as above but with XYZ parameter.
Scale Distance: This transformation allows scaling all the speakers inside a certain range of distances. It preserves the relative position of speakers.
Scale XYZ: Same as above but with XYZ parameters.
Rotation Azimuth: With this transform, we can apply a rotation to our speaker array.
Mirror: As its name implies, this transform creates a mirror of the speaker arrangement regarding a certain axis.
Linear uniform distribution along the selected axis: This transformation puts all the speakers on the same axis, with even space between them.
Circle: This transformation places all the speakers in the same circle, with an even space between them.
Sinus: This transformation creates a sinus shape with the speakers.